Vitamin D & Immunity: What You Need To Know
Could something as seemingly simple as a vitamin hold the key to unlocking a stronger, more resilient immune system? The evidence overwhelmingly suggests that Vitamin D is not just essential for bone health, but also a critical regulator of our immune responses, potentially shielding us from a range of threats.
The intricate dance between Vitamin D and the immune system is a subject that has captivated scientists for decades. While its role in bone health has long been established, the understanding of Vitamin D's immunomodulatory effects has undergone a significant evolution, particularly in recent years. This revised perspective has been fueled by emerging research, highlighting the complex interplay between this vital nutrient and our body's defense mechanisms. The implications are profound, suggesting that optimizing Vitamin D levels could play a crucial role in preventing or mitigating various health issues, from autoimmune diseases to infectious illnesses.
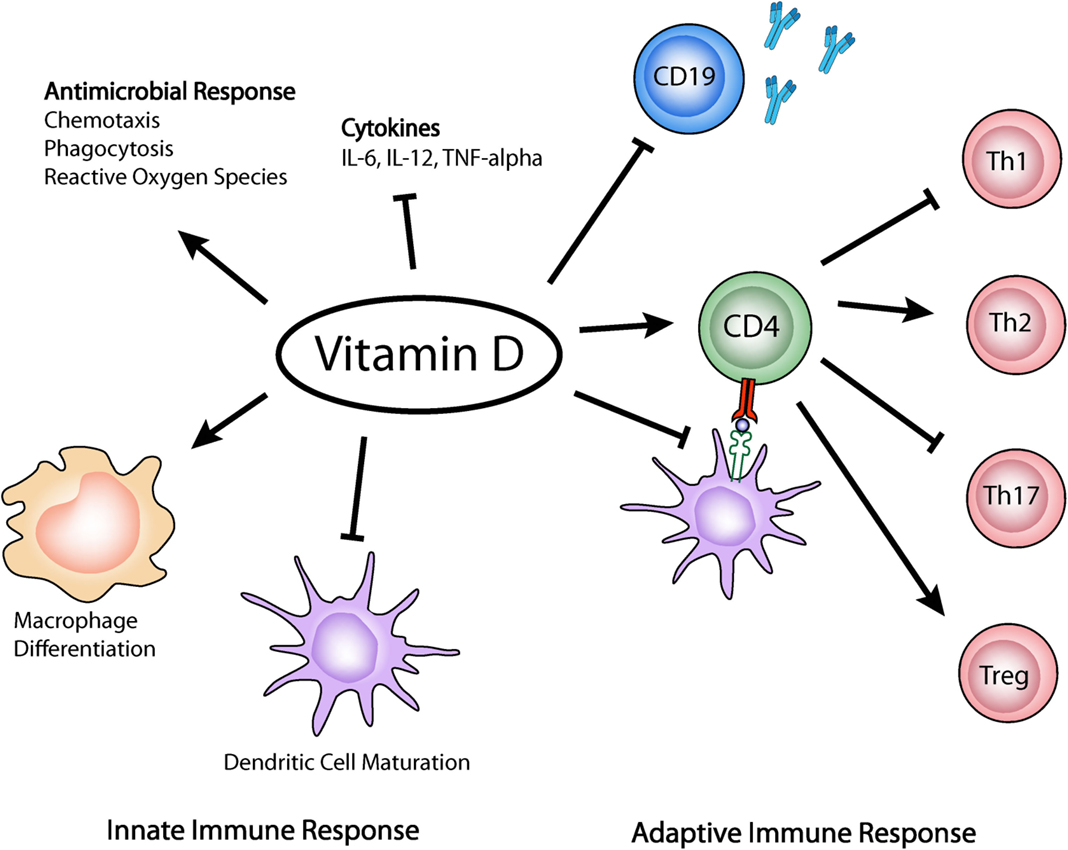
The core function of Vitamin D extends beyond its well-known role in skeletal health. It acts as an immunomodulatory hormone, influencing both the innate and adaptive immune responses. The innate immune system, the body's first line of defense, relies heavily on Vitamin D to fight off pathogens. Meanwhile, Vitamin D also fine-tunes the adaptive immune system, which is responsible for developing long-term immunity and immunological memory. The production of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), a key component of the innate immune response, is directly influenced by Vitamin D.
- Francis Escudero Net Worth 2024 How Rich Is The Politician
- Dhanushs Love Life From Aishwarya Split To New Rumors 2024
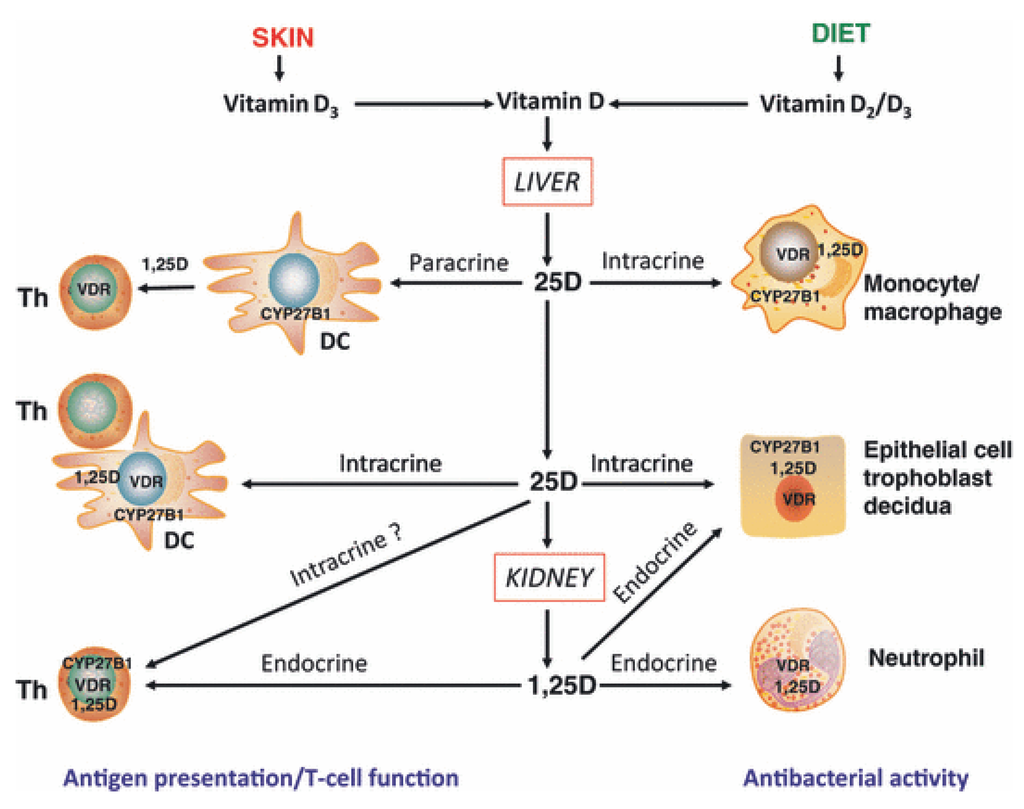
Several immune cells have the capacity to express the necessary enzymes (CYP27B1) to convert 25(OH)D to its active form, 1,25(OH)2D. This active form of Vitamin D then interacts with the Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) present on immune cells, initiating a cascade of events that modulate immune function. Vitamin D deficiency, conversely, has been consistently linked to a heightened risk of autoimmunity and a greater susceptibility to infections. This association underscores the importance of maintaining adequate Vitamin D levels for overall health and well-being.
The origins of Vitamin D can be traced to three main sources: the skin's synthesis after exposure to UVB light, dietary intake, and supplementation. For humans, the primary source of Vitamin D comes from the skin's production in response to sunlight. However, dietary sources and supplements are also crucial, especially for those with limited sun exposure or specific health needs. Food sources rich in Vitamin D include fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods.
The effects of Vitamin D extend to many kinds of immune cells like macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), T and B lymphocytes. These cells express the enzymes CYP27A1 and/or CYP27B1, enabling them to hydroxylate 25(OH)VD3 to 1,25(OH)2VD3. When 1,25(OH)2VD3 binds to the Vitamin D receptor (VDR) on these immune cells, it can act in an autocrine or paracrine way, directly influencing the activity of immune cells.
- Ray Charles Music Biography Top Hits Explore Now
- Ray Charles Life Legacy Soul Music Genius Explore Now
While the link between Vitamin D and bone health is well established, the exploration of Vitamin D's role in modulating the immune system has opened new avenues for understanding and preventing disease. From reducing inflammation to increasing immune cell activity, the effects of Vitamin D are far-reaching and significant. Understanding the mechanisms by which Vitamin D interacts with the immune system is critical for developing targeted strategies to improve human health.
It is important to acknowledge that the evidence is compelling, however, further research is needed to fully comprehend the breadth of Vitamin D's impact on immune function and its potential in a clinical setting. The role that variations in Vitamin D status plays in defining specific types of immune responses is a critical area of focus, it is crucial to understand how Vitamin D impacts the innate immunity.
Vitamin D's multifaceted effects, and its involvement in regulating both innate and adaptive immunity is what makes it so crucial. Beyond the traditional understanding of its impact on bone health, Vitamin D emerges as a key player in the intricate workings of our immune system. The impact of Vitamin D on immune system processes is a prime example of the broad spectrum of actions that Vitamin D has on physiologic and pathologic processes, which opens up the potential to boost immunity and reduce susceptibility to infections and autoimmune disorders.
To maintain healthy vitamin D levels, spend time in the sunlight and eat foods that contain this nutrient. You can also talk to your doctor about taking a vitamin d supplement.
Vitamin D is involved both in the regulation of the innate immunity as it enhances the body defence system against microbes and other pathogenic organisms, as well as in the modulation of the adaptive immune system through direct action on immune cells.
The potential implications of Vitamin D extend beyond its role in immune function. Current evidence suggests that Vitamin D intake may reduce the incidence and severity of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), juvenile diabetes mellitus, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and multiple sclerosis (MS).
The increasing volume of research dedicated to Vitamin D is a testament to its significance in the pursuit of health and well-being. As the understanding of this vital nutrient deepens, it becomes clearer that maintaining adequate Vitamin D levels could become a crucial strategy to support the immune system and overall health.
- Charlie Hurts Salary Net Worth What You Need To Know
- Trudeau Joly Rumors Swirl After Split Whats The Truth

The Role of Vitamin D in the Immune System as a Pro survival Molecule Clinical Therapeutics
Frontiers Immune Response Modulation by Vitamin D Role in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Nutrients Free Full Text Vitamin D and Immune Function