Vitamin D & Immunity: Your Guide To A Stronger Immune System
Can a simple vitamin truly be the key to unlocking a stronger immune system and a healthier life? The answer, backed by a wealth of scientific evidence, is a resounding yes: Vitamin D plays a critical, multifaceted role in immune regulation, impacting our ability to fight off infections and even preventing autoimmune diseases.
The realm of immunology has long recognized the intricate dance of cells, molecules, and processes that make up our body's defense system. Vitamin D, often lauded for its contributions to bone health, is now increasingly understood as a pivotal player in this complex choreography. Research has shown that vitamin D has numerous effects on the cells within the immune system, from the front-line responders like macrophages and dendritic cells to the specialized forces of T and B cells. This understanding has broadened our perspective, moving beyond the traditional focus on calcium and bone health to encompass the vitamin's profound influence on overall well-being.
To further explore the vital role of Vitamin D, let's consider the following details:
- Secure Remote Access Your Guide To Remoteiot Alternatives
- Remoteiot Securely Access Manage Your Devices Anywhere
| Category | Details |
| Overview | Vitamin D, often called the "sunshine vitamin," is a fat-soluble nutrient essential for various bodily functions, most notably bone health and immune regulation. It exists in two primary forms: Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). |
| Sources | Vitamin D is synthesized in the skin upon exposure to sunlight (specifically UVB rays). Dietary sources include fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), egg yolks, fortified foods (milk, cereals), and supplements. |
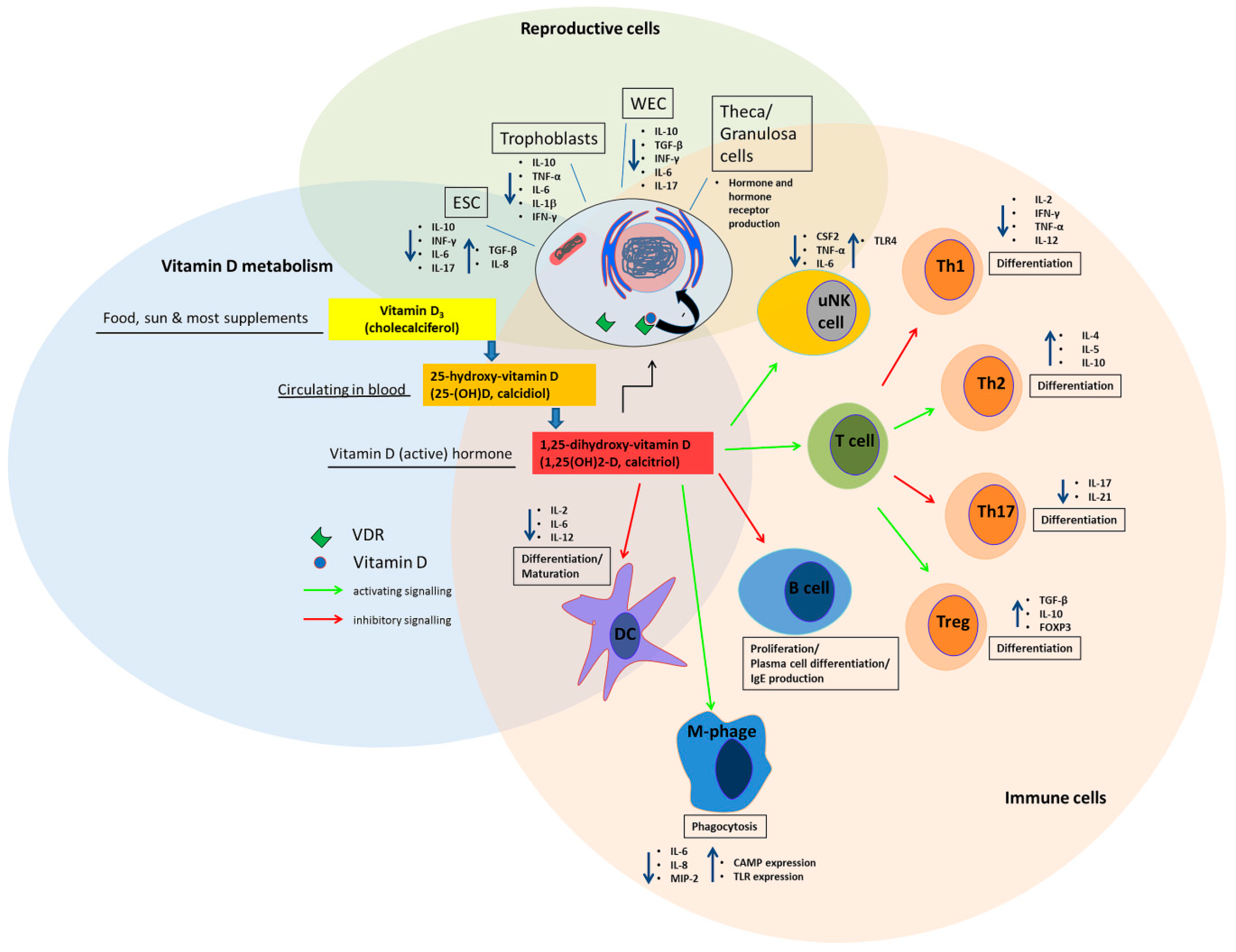
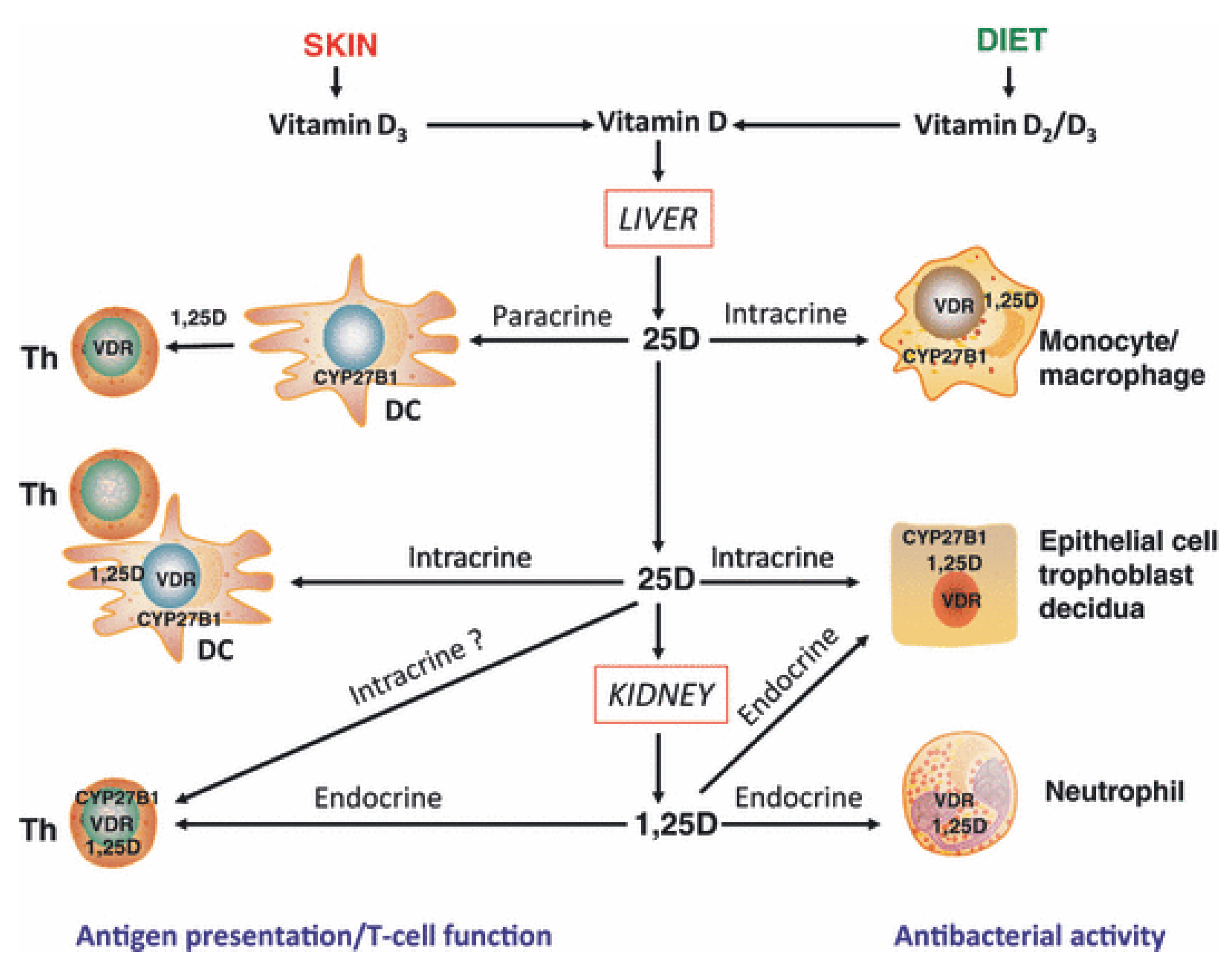
| Absorption and Metabolism | Vitamin D is absorbed from the gut and transported to the liver, where it is converted to 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D), the primary form measured in blood tests. This form is then further converted in the kidneys and other tissues to the active form, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D). |
| Immune System Effects |
|
| Deficiency | Widespread, associated with increased autoimmunity, increased susceptibility to infection, and increased incidence or aggravation of certain health conditions. |
| Supplementation |
|
| Health Benefits |
|
| Forms of Vitamin D |
|
| Vitamin D and Sunlight |
|
Reference: Mayo Clinic - Vitamin D
The significance of vitamin D's impact on the immune system is a prime example of its broad-spectrum actions on physiological and pathological processes. While it is a key regulator of bone and mineral homeostasis, its influence on the immune system illustrates a role beyond bone health. The ability of vitamin D to modulate both innate and adaptive immune responses underscores its importance in overall health. Understanding how vitamin D aids the immune system reveals a multifaceted role in enhancing immunity while preventing deficiencies that are associated with increased susceptibility to infections and autoimmune diseases.
The evidence is compelling: Vitamin D can interact with immune cells, affecting genes that regulate inflammation and altering the immune system's response. Consequently, it makes sense to investigate whether supplemental vitamin D is an effective way to treat or prevent autoimmune diseases. Deficiencies in vitamin D are linked with increased autoimmunity and a higher susceptibility to infection. The simple act of ensuring adequate vitamin D levels can have a powerful impact.
- Trudeau Joly Rumors Swirl After Split Whats The Truth
- Kristi Noems Husband Bryons Life Their 30 Year Marriage
The immune system is our body's sophisticated defense network, working tirelessly to protect us from a host of threats. Having a strong immune system, especially during cold and flu season, can help reduce the risk of getting sick. A robust immune system will bolster your body against sicknesses like colds and the flu. It can also help you recover from injury and keep your energy level high. Essentially, taking sufficient levels of vitamin D can help fortify your immune system, which is why we need to make sure were getting enough every dayparticularly during winter when sunlight exposure is limited.
In regions with limited sunlight, our bodies rely less on natural production. Vitamin D3, the form produced by our bodies, is particularly crucial in these environments. Supplementation may be necessary to maintain optimal levels, especially for individuals in these areas. This nutrient is especially important for immune system health, leaving many people wondering whether supplementing with vitamin D may help reduce the risk of contracting illnesses.
The process of activating and deactivating the immune system is complex, and vitamin D plays a pivotal role in this. Research teams have identified the role of vitamin D in the activation of T cells as a major breakthrough. Moreover, vitamin D reduces immune cell activity, demonstrating a nuanced effect that contributes to immune system balance. Researchers at the University of Edinburgh looked at how vitamin D affects two types of cells, called dendritic cells and T cells. These cells are both part of our immune system.
The connection between vitamin D and immune system function is now well-established, and its benefits are undeniable. It supports healthy bones, teeth, and a healthy immune system. In addition to aiding the bodys absorption of calcium and phosphorus, vitamin D has been shown to support the immune system in various ways. The impact that vitamin D has on the immune system is a prime example of the broad spectrum of actions that vitamin D has on physiologic and pathologic processes.
Recent epidemiological evidence has indicated a significant association between vitamin D deficiency and an increased incidence, or aggravation, of various health issues. The impact of vitamin D is not limited to preventing infections; it also helps in the fight against specific diseases. The role of vitamin D in supporting the immune system is increasingly recognized. With respect to in vitro, overwhelming evidence exists for a physiological role for the vitamin D system in immune regulation, and immune modulation can be observed by exposing immune cells to pharmacological doses of vitamin D metabolites. Vitamin D functions within the immune system to regulate immune cell activity and produce antimicrobial peptides.
But the benefits don't end there. New research published in Frontiers in Immunology concludes that vitamin D can help the immune system fight tuberculosis. Daily intake can increase immune system function and significantly reduces the risk of viral respiratory infections, even in the elderly. These findings underscore the versatility of vitamin D and the diverse ways it impacts our health.
Considering the widespread nature of vitamin D deficiency, addressing it becomes a critical step toward better health. While various factors influence how much vitamin D you need, taking a daily dose of this nutrient can significantly improve your immune function. Vitamin D deficiency is widespread, with studies showing that many adults fall below the estimated average requirement. It is now clear that vitamin D has important roles in addition to its classic effects on calcium and bone homeostasis. Vitamin D deficiency treatment and supplementation is more critical than ever.
Research shows that taking vitamin D once a week (mega doses, bolus doses), is not only ineffective but can lead to immune system compromise. Instead, daily intake is recommended to make sure youre getting enough. Vitamin D3 is often considered more effective at enhancing serum levels of vitamin D in the blood, making it important for those living in regions with limited sunlight.
Given the evidence, why take a chance at being deficient in vitamin D? From bone health to immune regulation, the benefits are clear. The multifaceted role of vitamin D in our bodies emphasizes its importance in promoting overall health and well-being.

The Role of Vitamin D in the Immune System as a Pro survival Molecule Clinical Therapeutics
Nutrients Free Full Text Vitamin D Effects on the Immune System from Periconception through
Nutrients Free Full Text Vitamin D and Immune Function